“A building in which the ceiling heights are all the same is virtually incapable of making people comfortable.”
It is all too often that the Common House is designed and built with the least funds (many communities prioritize the money for individual units) and therefore, the overall enclosure of the Common House is constructed with the idea that a future mezzanine or second floor will be added later. The resulting spaces for dining, conversation, and meal preparation all occur under a single ceiling.
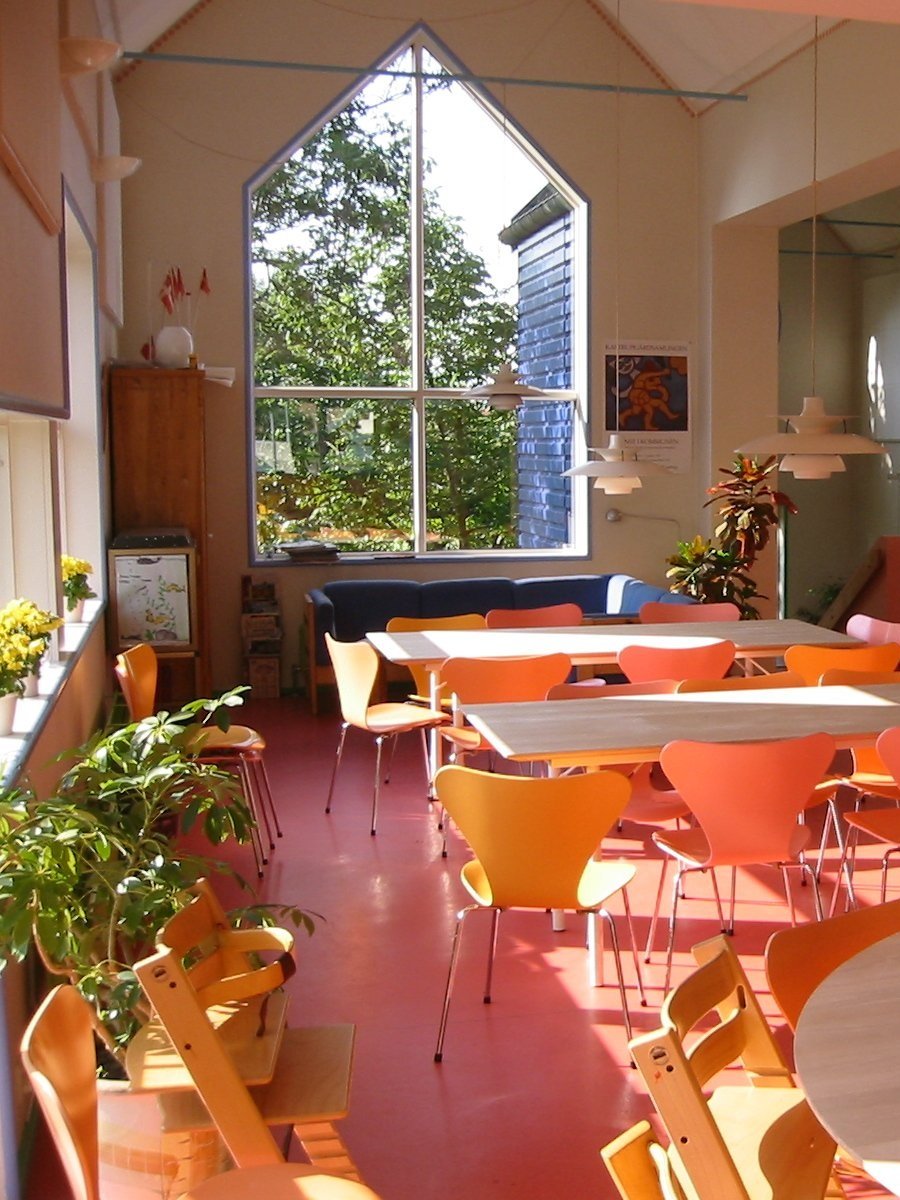
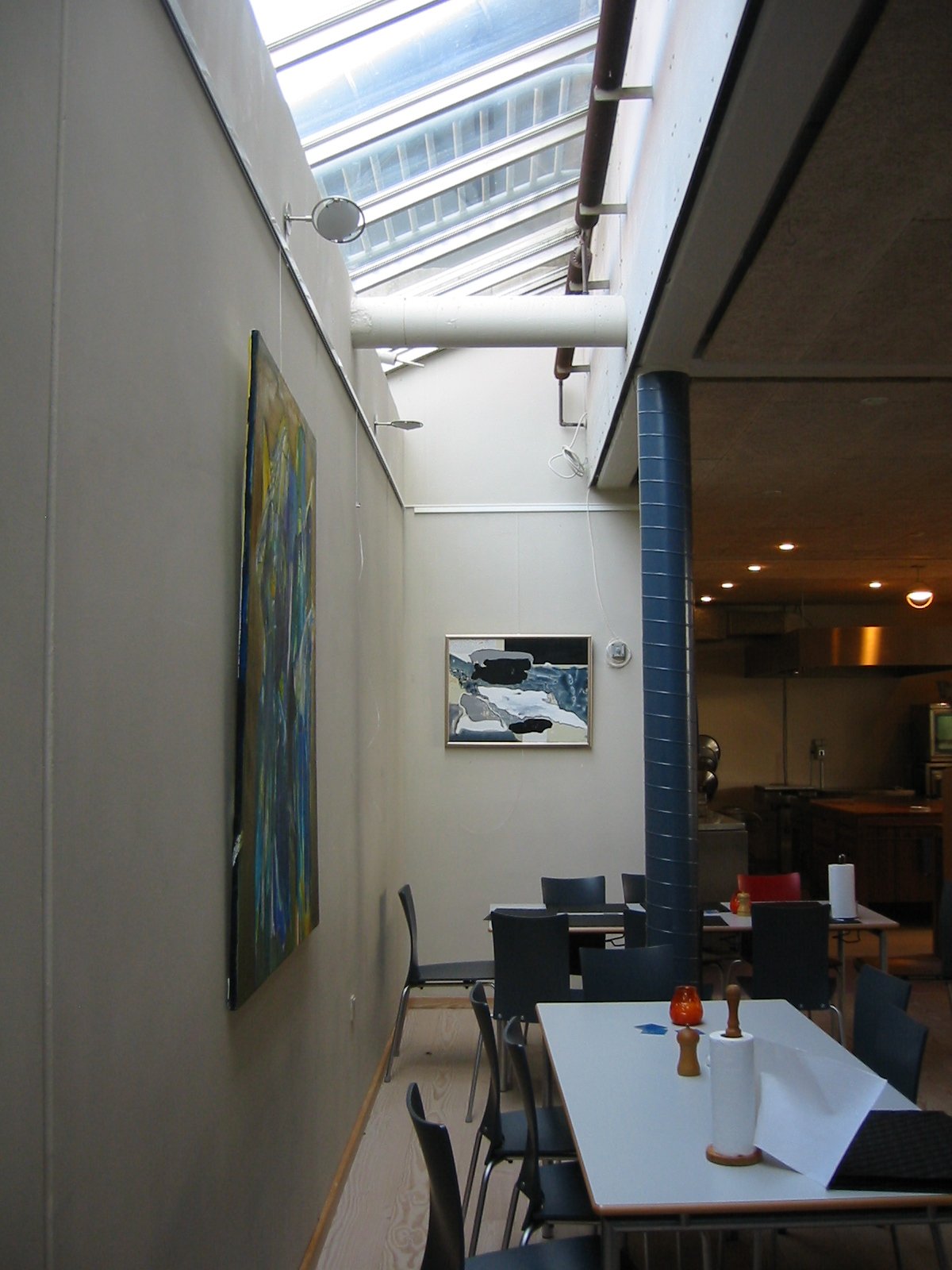
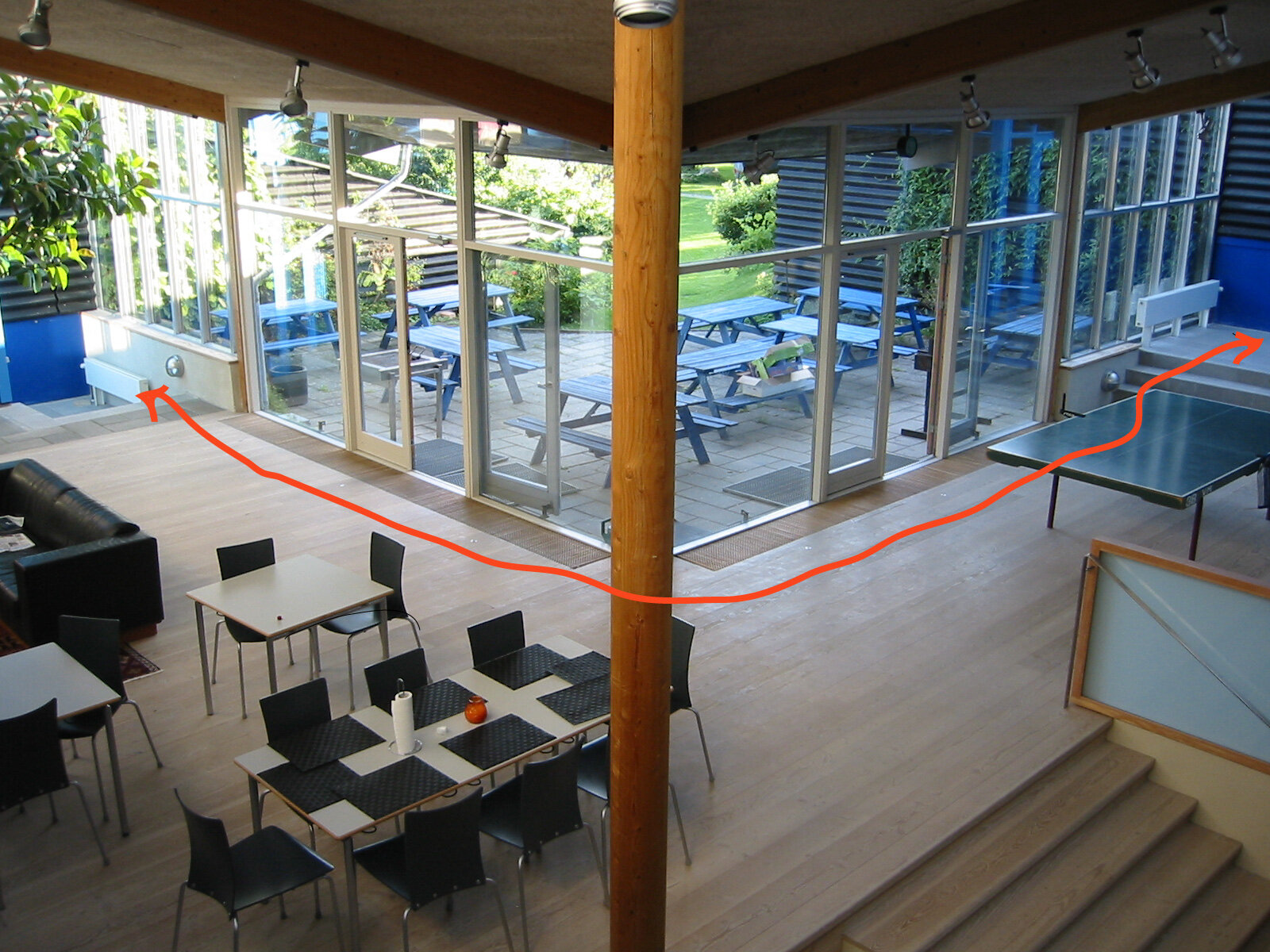
Provide a variety of ceiling heights that are appropriate for the functions. The dining room may want to be a grand space with high ceilings, however, the kitchen will be more functional with lower ceilings. In addition, smaller seating groups for conversation are not inviting if they are located in a cavernous room with the same ceiling height as the dining room.
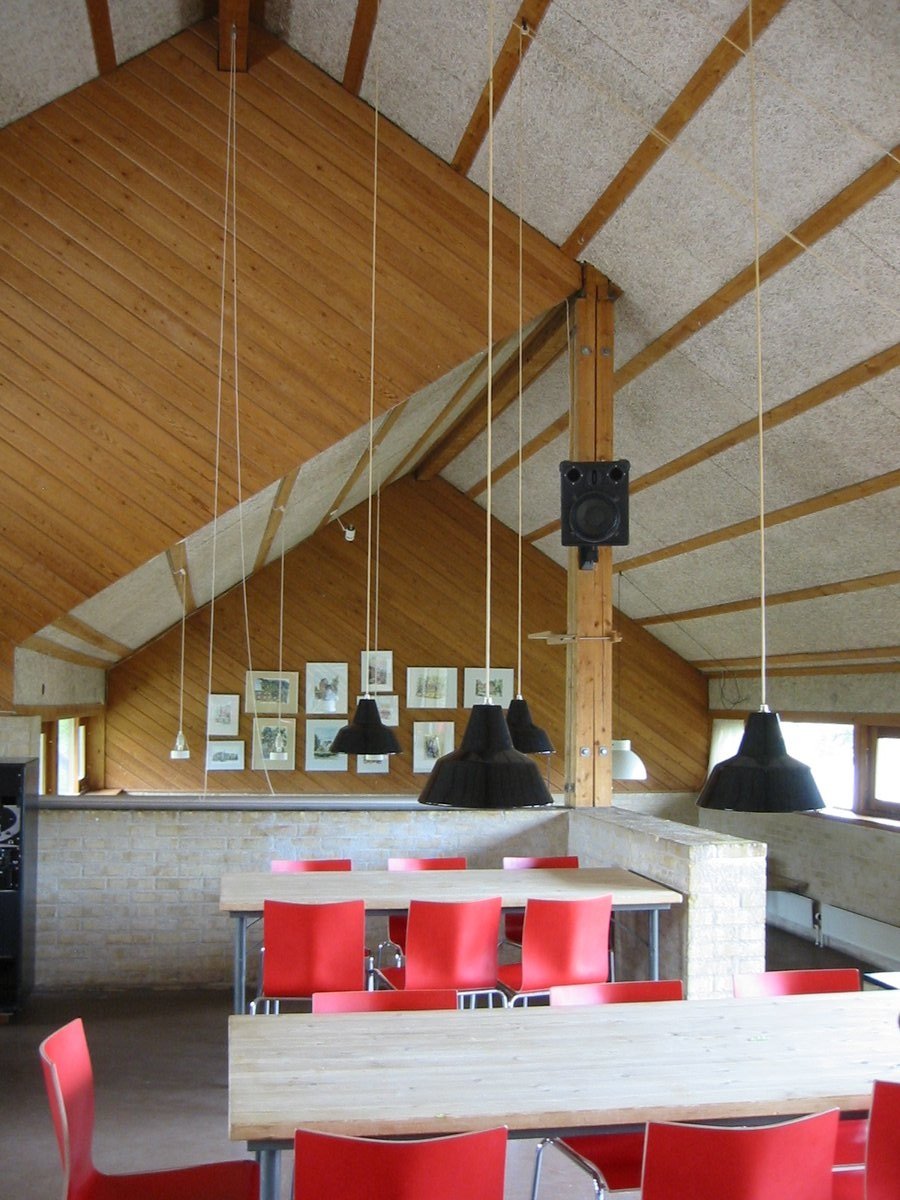
Bakken, a cohousing community in Northern Denmark, is comprised of duplexes, triplexes and a large common house. In the common house, the dining and seating area all occur under the same ceiling. The seating area is not welcoming and did not encourage residents to linger and talk. However, over half of the dining room floor framing had been installed with the idea that the second-floor mezzanine would be extended. While the project was never completed, the major framing elements were left in place creating an implied ceiling. The tables under this “lower” ceiling felt more intimate.
The height of a ceiling can also determine the intimacy of a space. The ceiling must be proportionate to the size of the room - a small room with a tall ceiling will feel equally uncomfortable as a large room with a low ceiling. The original pattern describes rules of thumb for ideal width-to-height ratios. The acoustics of any room are affected by the ceiling height and room proportion and should be given specific attention during design.